ASP.NET Core Blazorでsqlserverに接続してデータを表示する
- 作成日 2022.01.19
- 更新日 2022.01.21
- ASP.NET Core
- ASP.NET Core

ASP.NET Coreを使ってBlazorでsqlserverに接続してデータを表示する手順を記述してます。.NET Coreのバージョンは6を使用してます。
環境
- OS windows10 pro
- IDE Visual Studio 2022
- .NET Core 6
- Sql Server 2019
Blazorプロジェクト作成
プロジェクト作成時に「Blazor WebAssembly」アプリを選択します。
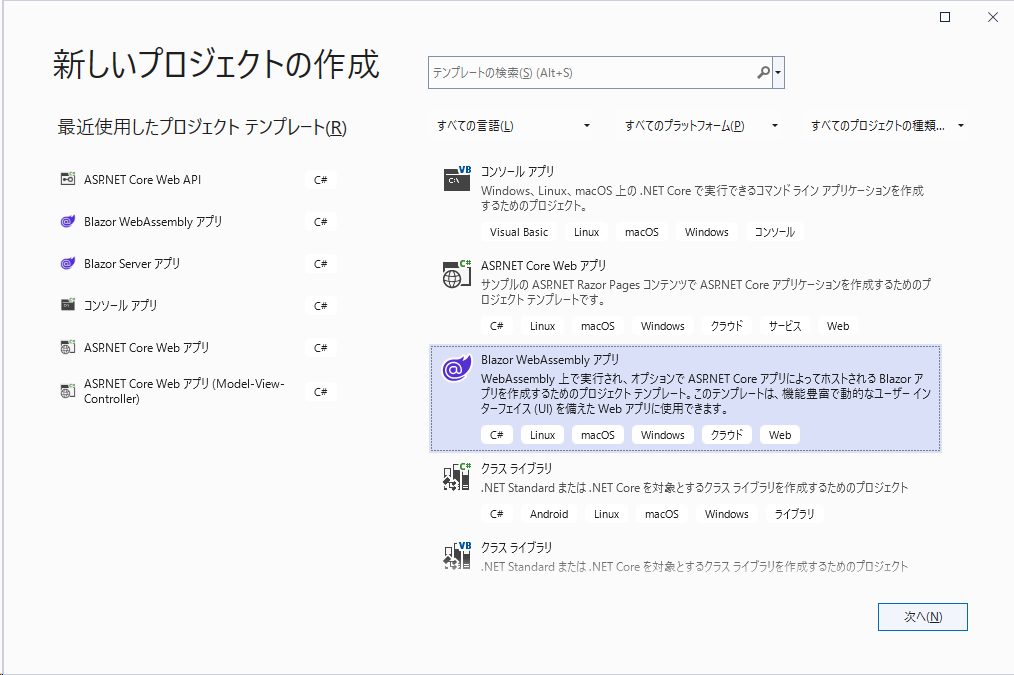
任意の名前でプロジェクトを作成します。
※ここでは「TestBlazor」という名前で作成してます。
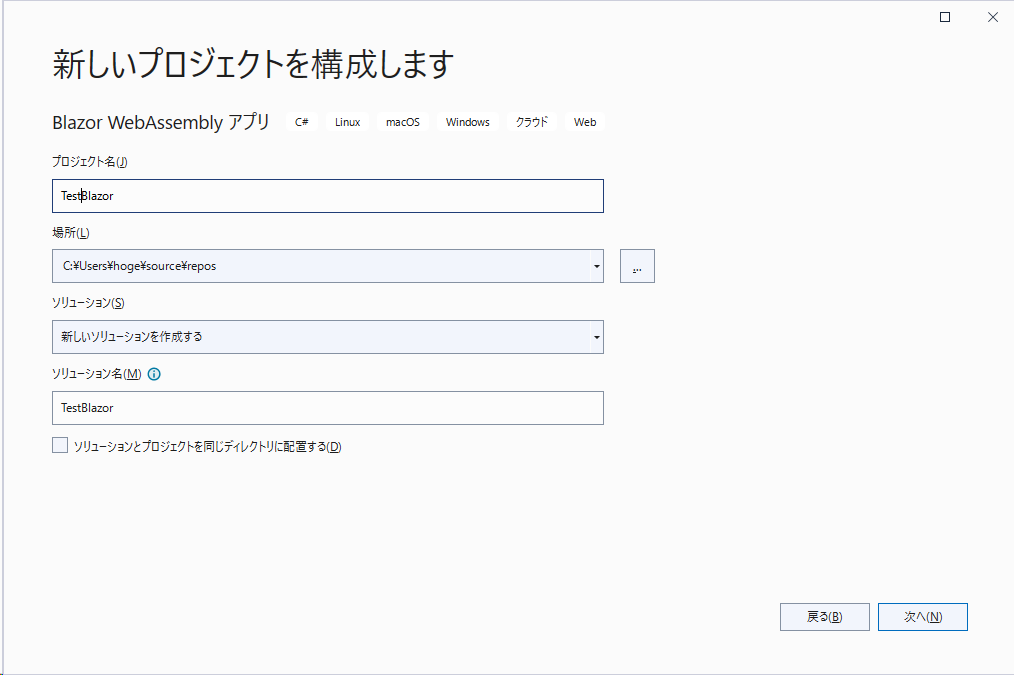
「ASP.NET Coreでホストされた」をチェックして、「作成」ボタンを押下します。
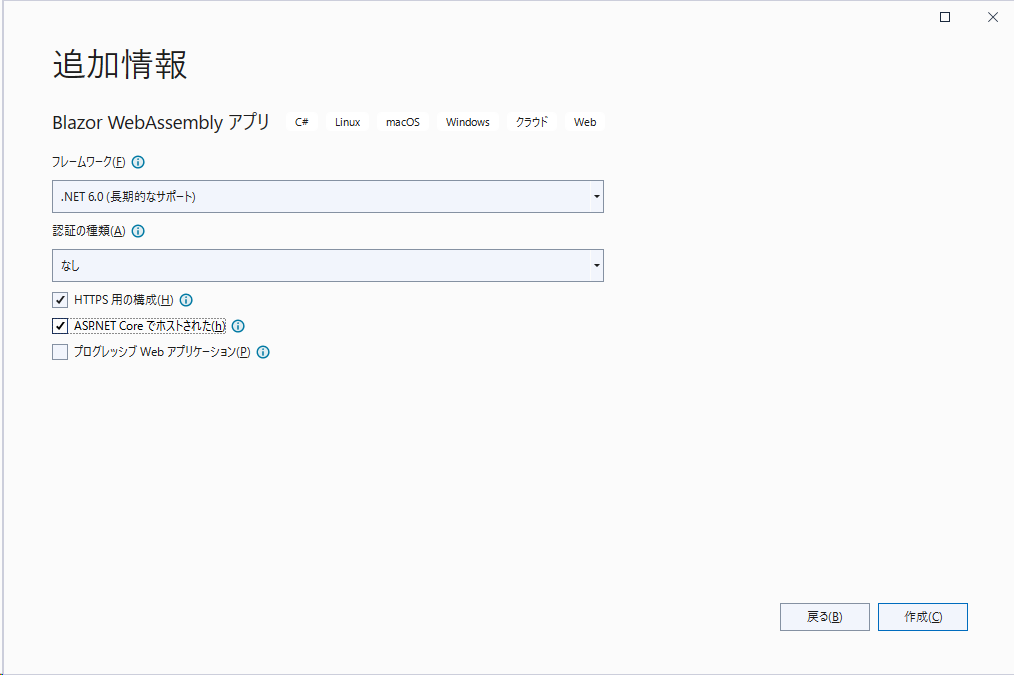
ASP.NET Core Blazor WebAssemblyでプロジェクトを作成すると、クライアント用とサーバー用と共通の3つのプロジェクトが作成されます。
そのままビルドして実行すると、サンプルを起動することができます。
使用するSqlServer
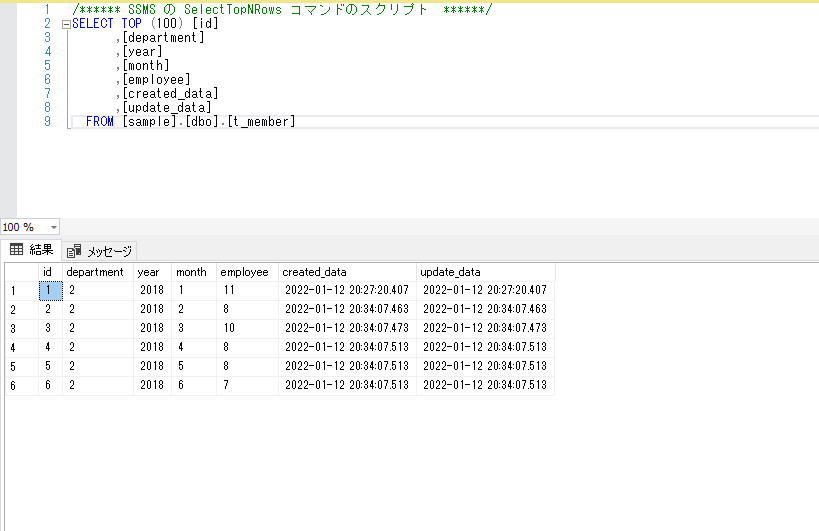
DB「sample」にある「t_member」というテーブルを使用して、データを表示してみます。
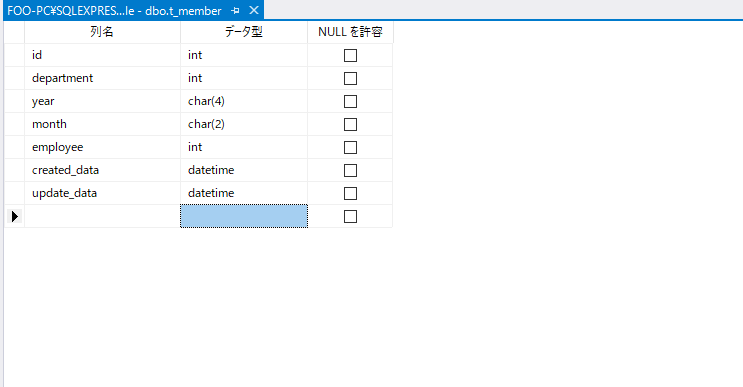
以下のデータが存在します。
パッケージ追加
事前に使用するパッケージを追加しておきます。
「ツール」 > 「NuGet パッケージ マネージャー」 > 「パッケージ マネージャー コンソール」を選択します。
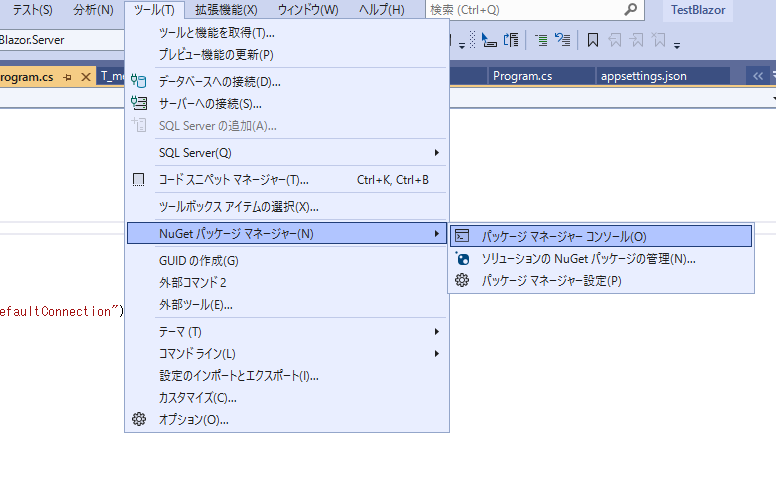
以下の2つを「Server」の方のプロジェクトに追加します。
PM> Install-Package -ProjectName TestBlazor.Server -Id Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer
PM> Install-Package -ProjectName TestBlazor.Server -Id Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools接続情報
sqlserverと接続できるように接続情報を用意します。
「appsettings.json」に、以下のコードを追加します。
「ConnectionStrings」を追加します。
{
"Logging": {
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Information",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore": "Warning"
}
},
"AllowedHosts": "*",
"ConnectionStrings": {
"DefaultConnection": "Server=192.168.xxx.xxx;Database=sample;User ID=sa;Password=password;"
}
}Model作成
まずはModelを作成します。「Shared」に「Models」フォルダを作成して
「T_member.cs」というファイルを作成します。

以下の内容でコードを記述します。
namespace TestBlazor.Shared.Models
{
public class T_member
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public int Department { get; set; }
public string? Year { get; set; }
public string? Month { get; set; }
public int Employee { get; set; }
public DateTime Created_data { get; set; }
public DateTime Update_data { get; set; }
}
}名前付けのルール違反と警告されますが、ここではこのまま進めます。

コンテキストクラス作成
次に、コンテキストクラスを作成します。「Server」フォルダ配下に「AppDbContext.cs」というファイルを作成します。

さきほど作成した「Model」を登録しておきます。
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using TestBlazor.Shared.Models;
namespace TestBlazor.Server.Data
{
public class AppDbContext : DbContext
{
public AppDbContext(DbContextOptions options) : base(options)
{
}
public DbSet<T_member> T_member { get; set; }
}
}サービス登録
サービスに、コンテキストを登録します。
「Program.cs」に
さきほど作成した接続情報「DefaultConnection」を使用して「AppDbContext」を登録します。
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.ResponseCompression;
using TestBlazor.Server.Data;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Add services to the container.
builder.Services.AddControllersWithViews();
builder.Services.AddRazorPages();
// 追加
builder.Services.AddDbContext<AppDbContext>(
options => options.UseSqlServer(
builder.Configuration.GetConnectionString("DefaultConnection")
)
);
var app = builder.Build();
// Configure the HTTP request pipeline.
if (app.Environment.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseWebAssemblyDebugging();
}
else
{
app.UseExceptionHandler("/Error");
// The default HSTS value is 30 days. You may want to change this for production scenarios, see https://aka.ms/aspnetcore-hsts.
app.UseHsts();
}
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseBlazorFrameworkFiles();
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseRouting();
app.MapRazorPages();
app.MapControllers();
app.MapFallbackToFile("index.html");
app.Run();
Api作成
「Controllers」フォルダに「スキャフォールディング」を使用して、Controllerを作成します。
「Controllers」フォルダを右クリックして「新規スキャフォールディングアイテム」をクリックします。
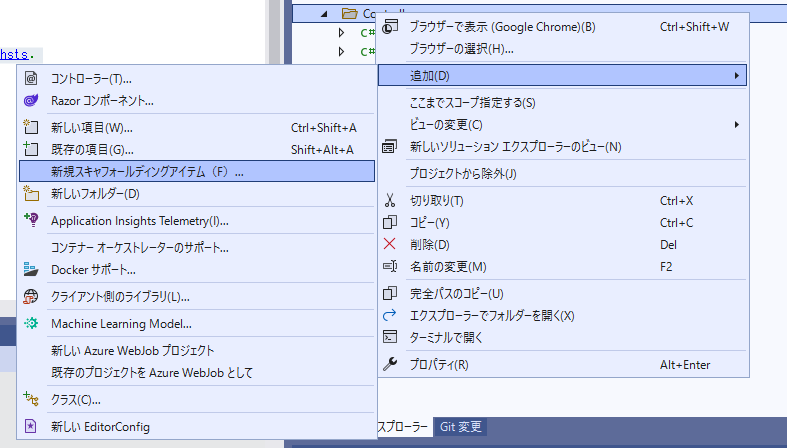
「Entity Frameworkを使用したアクションがある APIコントローラー」を、選択して追加をクリックします。
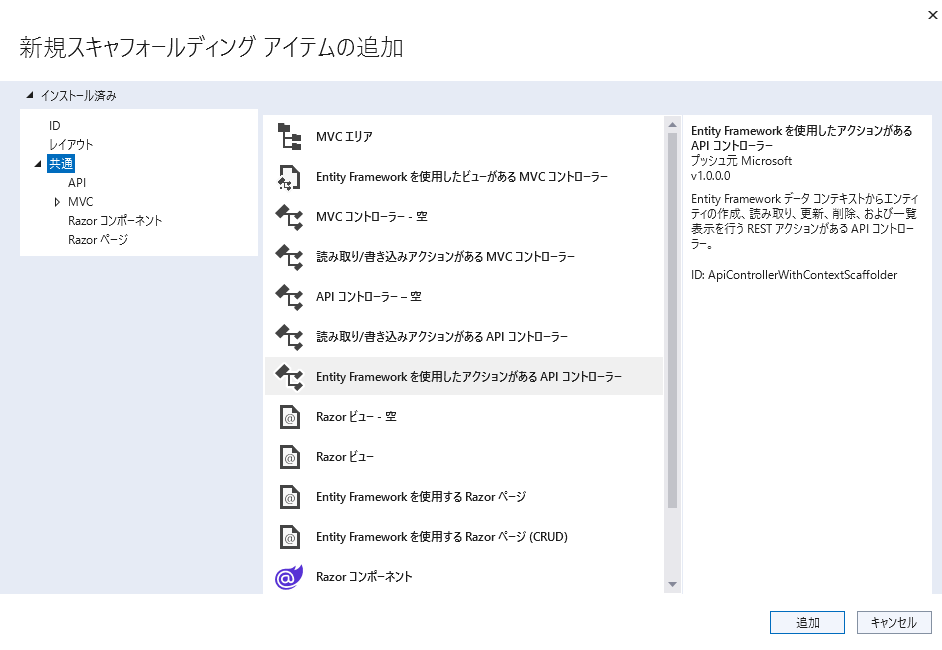
「T_memberController.cs」という名前を入力して「追加」をクリックします。
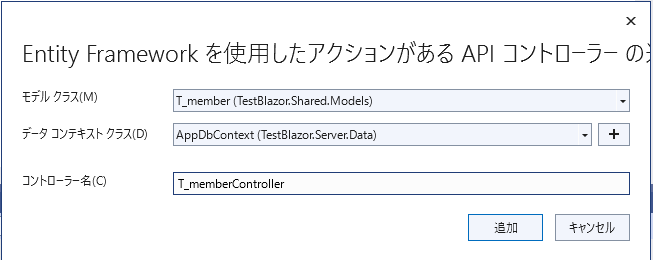
これでAPIが使用できるようになるので、一度確認してみます。
#nullable disable
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using TestBlazor.Server.Data;
using TestBlazor.Shared.Models;
namespace TestBlazor.Server.Controllers
{
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class T_memberController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly AppDbContext _context;
public T_memberController(AppDbContext context)
{
_context = context;
}
// GET: api/T_member
[HttpGet]
public async Task<ActionResult<IEnumerable<T_member>>> GetT_member()
{
return await _context.T_member.ToListAsync();
}
// GET: api/T_member/5
[HttpGet("{id}")]
public async Task<ActionResult<T_member>> GetT_member(long id)
{
var t_member = await _context.T_member.FindAsync(id);
if (t_member == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
return t_member;
}
// PUT: api/T_member/5
// To protect from overposting attacks, see https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=2123754
[HttpPut("{id}")]
public async Task<IActionResult> PutT_member(long id, T_member t_member)
{
if (id != t_member.Id)
{
return BadRequest();
}
_context.Entry(t_member).State = EntityState.Modified;
try
{
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
}
catch (DbUpdateConcurrencyException)
{
if (!T_memberExists(id))
{
return NotFound();
}
else
{
throw;
}
}
return NoContent();
}
// POST: api/T_member
// To protect from overposting attacks, see https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=2123754
[HttpPost]
public async Task<ActionResult<T_member>> PostT_member(T_member t_member)
{
_context.T_member.Add(t_member);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
return CreatedAtAction("GetT_member", new { id = t_member.Id }, t_member);
}
// DELETE: api/T_member/5
[HttpDelete("{id}")]
public async Task<IActionResult> DeleteT_member(long id)
{
var t_member = await _context.T_member.FindAsync(id);
if (t_member == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
_context.T_member.Remove(t_member);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
return NoContent();
}
private bool T_memberExists(long id)
{
return _context.T_member.Any(e => e.Id == id);
}
}
}API確認
デバックを実行して「api/t_member」にアクセスしてみます。
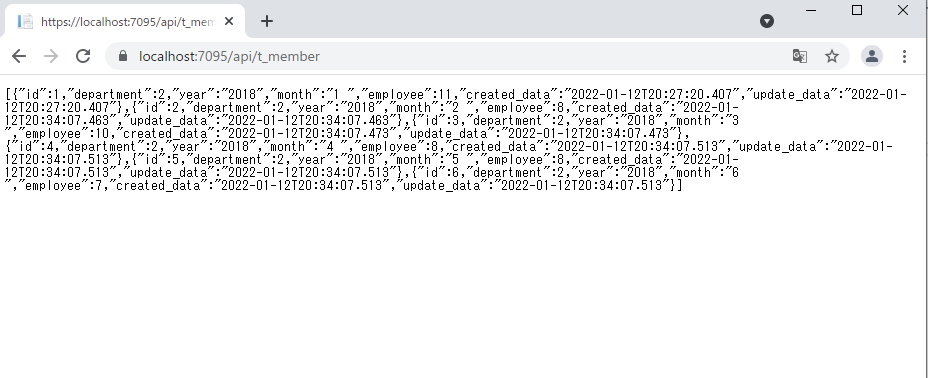
jsonが表示されると思います。
Client側実装
Apiが確認できたので、ここからClient側を構築していきます。
デザインテンプレートに「AntDesign」を使用するのでインストールして、利用できるようにしておきます。
PM> Install-Package -ProjectName TestBlazor.Client -Id AntDesign使用できるように「wwwroot」配下の「index.html」に、CSSとJSを追加します。
以下を追加します。
<link href="_content/AntDesign/css/ant-design-blazor.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<script src="_content/AntDesign/js/ant-design-blazor.js"></script>ソースコード画像
※ここの「index.html」に記述されている「Loading…」が一番初めに表示されます。

「Shared」ファルダ配下の「_Imports.razor」にも追加します。
「using AntDesign」を追加します。
@using System.Net.Http
@using System.Net.Http.Json
@using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Components.Forms
@using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Components.Routing
@using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Components.Web
@using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Components.Web.Virtualization
@using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Components.WebAssembly.Http
@using Microsoft.JSInterop
@using TestBlazor.Client
@using TestBlazor.Client.Shared
@using AntDesign「Program.cs」にも追加して、サービスにも登録します。
「builder.Services.AddAntDesign()」を追加します。
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Components.Web;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Components.WebAssembly.Hosting;
using TestBlazor.Client;
var builder = WebAssemblyHostBuilder.CreateDefault(args);
builder.RootComponents.Add<App>("#app");
builder.RootComponents.Add<HeadOutlet>("head::after");
builder.Services.AddScoped(sp => new HttpClient { BaseAddress = new Uri(builder.HostEnvironment.BaseAddress) });
builder.Services.AddAntDesign(); //追加
await builder.Build().RunAsync();コンポーネントも「App.razor」に追加しておきます。
「AntContainer」を追加します。
<Router AppAssembly="@typeof(App).Assembly">
<Found Context="routeData">
<RouteView RouteData="@routeData" DefaultLayout="@typeof(MainLayout)" />
<FocusOnNavigate RouteData="@routeData" Selector="h1" />
</Found>
<NotFound>
<PageTitle>Not found</PageTitle>
<LayoutView Layout="@typeof(MainLayout)">
<p role="alert">Sorry, there's nothing at this address.</p>
</LayoutView>
</NotFound>
</Router>
<AntContainer />ページ作成
ページを作成してみます。
「Pages」を右クリックしてRazorコンポーネントを追加します。
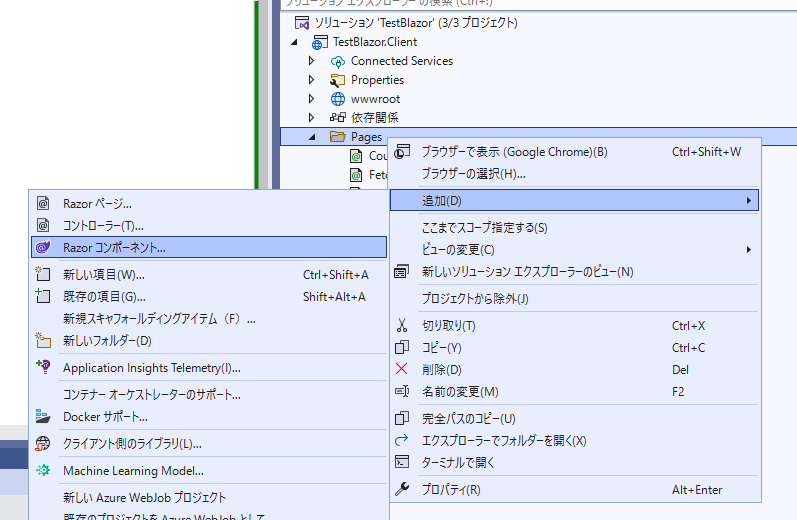
「Member.razor」という名前で作成します。
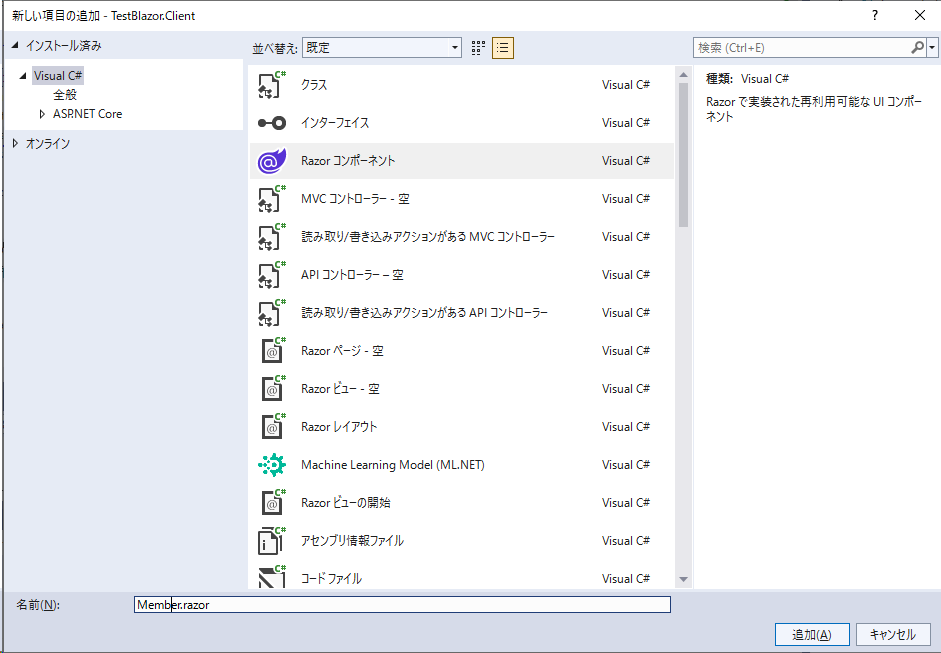
「AntDesign」のサイトを参考にtableを作成します。
@page "/member"
@using TestBlazor.Shared.Models
@inject HttpClient Http
@if (t_member == null)
{
<p><em>Loading...</em></p>
}
else
{
<Table TItem="T_member" DataSource="@t_member">
<Column @bind-Field="@context.Id" />
<Column @bind-Field="@context.Department" Sortable />
<Column @bind-Field="@context.Year" />
<Column @bind-Field="@context.Month" />
<Column @bind-Field="@context.Employee" />
<Column @bind-Field="@context.Created_data" />
<Column @bind-Field="@context.Update_data" />
</Table>
}
@code {
private List<T_member>? t_member;
protected override async Task OnInitializedAsync()
{
t_member = await Http.GetFromJsonAsync<List<T_member>>("api/T_member");
}
}
これで「/member」にアクセスすると、以下のテーブルが表示されると思います。
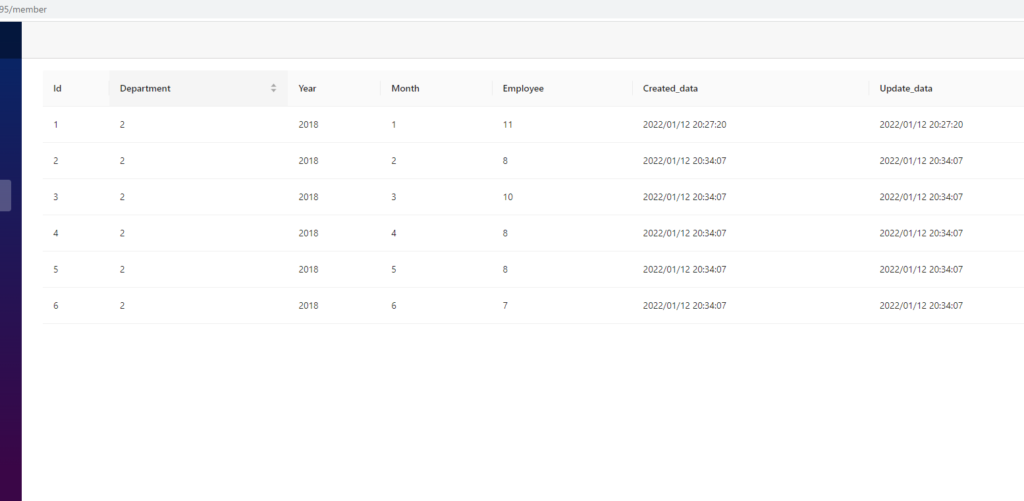
-
前の記事

MySQL jsonデータからkeyを指定してvalueを取得する 2022.01.19
-
次の記事

javascript lodashでメソッドチェーンを任意のタイミングで実行する 2022.01.20







コメントを書く